The above video (the rule for this text) covers an intensive instance mission exhibiting you learn how to construct a Chainlink NFT. As chances are you’ll already know, Chainlink is an oracle blockchain mission providing a number of neat options. One among these is Chainlink’s VRF (verifiable random operate), which can be one of many major instruments we’ll use on this tutorial to mint random non-fungible tokens. Basically, we’ll create a dapp with an NFT-minting good contract incorporating Chainlink’s VRF.
For our contract to construct the NFT, we additionally want NFT-representing recordsdata (photos) and metadata recordsdata, which we’ll retailer in IPFS. That is the place Moralis’ IPFS API enters the equation. For this, the next code snippet will do the heavy lifting:
end result = evm_api.ipfs.upload_folder( api_key=api_key, physique=physique, )
With the recordsdata in IPFS, we’ll have the ability to embrace metadata URIs in our good contract. That is the preliminary Solidity line of code of our good contract:
contract RandomNFT is ERC721URIStorage, VRFConsumerBaseV2, Ownable {
So far as our dapp goes, it should include a JavaScript frontend and a Python backend. In terms of fetching on-chain knowledge, Moralis’ final NFT API will simplify issues through the next traces of code:
end result = evm_api.nft.get_nft_owners( api_key=api_key, params=params, )
In case you are able to tackle at present’s Chainlink NFT tutorial, create your free Moralis account and comply with our lead!
TRUSTED BY INDUSTRY LEADERS

Overview
Shifting ahead, we’ll dive into the steps you must full to construct a Chainlink NFT minter. This dapp randomly takes NFT-representing recordsdata and their metadata and mint NFTs when customers click on on the “Mint!” button on the frontend. Now, to make such a dapp work, there are a lot of facets to cowl, so the next description will spotlight the important facets, and check with the above video for particulars. Listed below are the core steps that you must cowl to finish our Chainlink NFT tutorial:
- Arrange your Chainlink VRF.
- Write your distinctive good contract script in Solidity or copy our template.
- Put together the NFT-representing and metadata recordsdata and add them to IPFS or use our instance recordsdata.
- Deploy your Solidity good contract that may construct a Chainlink NFT.
- Construct frontend and backend parts of an NFT minting dapp that ties all of it collectively.
Following our lead, you additionally want a number of instruments to finish the above steps. These embrace Chainlink VRF, MetaMask, Visible Studio Code (VSC), Brownie or Remix, an Ethereum faucet, a Chainlink faucet, and Moralis. We may also do a fast demonstration of the ultimate construct within the “Construct a Chainlink NFT” part.
Under the precise tutorial, you can too discover a number of sections that may enable you higher perceive the theoretical facets of at present’s subject. That is the place you may be taught what Chainlink and Chainlink NFTs are and discover the gist of the aforementioned instruments.

Chainlink NFT Tutorial – Construct a Chainlink NFT
As outlined above, we are able to dive proper into step one – establishing your Chainlink VRF. Use the video above, beginning at 2:21, for extra particulars about VRF. Now, begin by opening Chainlink’s subscription supervisor from Chainlink’s docs:
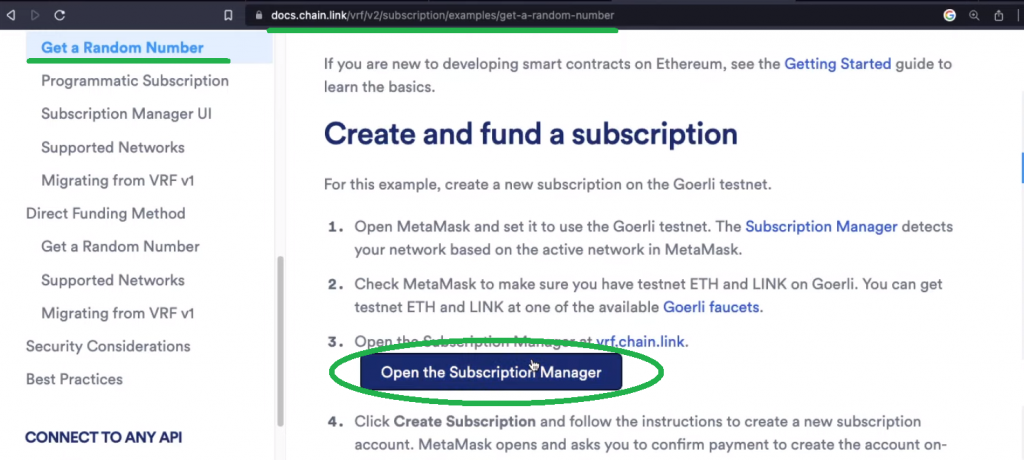
Subsequent, choose “Ethereum Goerli” and join your MetaMask through the “Join pockets” button:
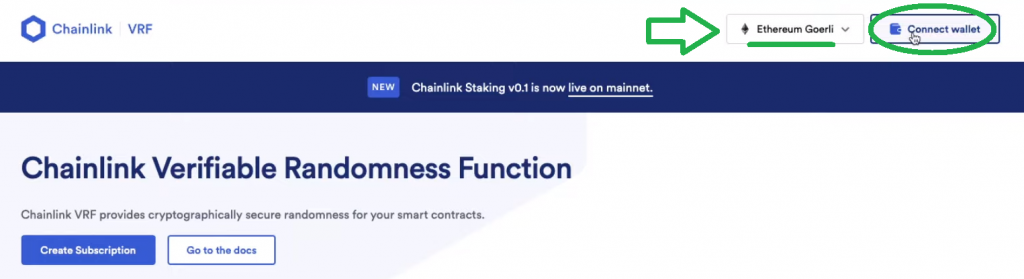
As soon as your pockets is linked, click on on “Create Subscription” and make sure the transaction together with your MetaMask pockets. Then, you must ensure that your account has sufficient funds. Since you might be on the testnet, you should use the Chainlink testnet faucet to get testnet LINK. Simply join your pockets and request ten testnet LINK tokens:
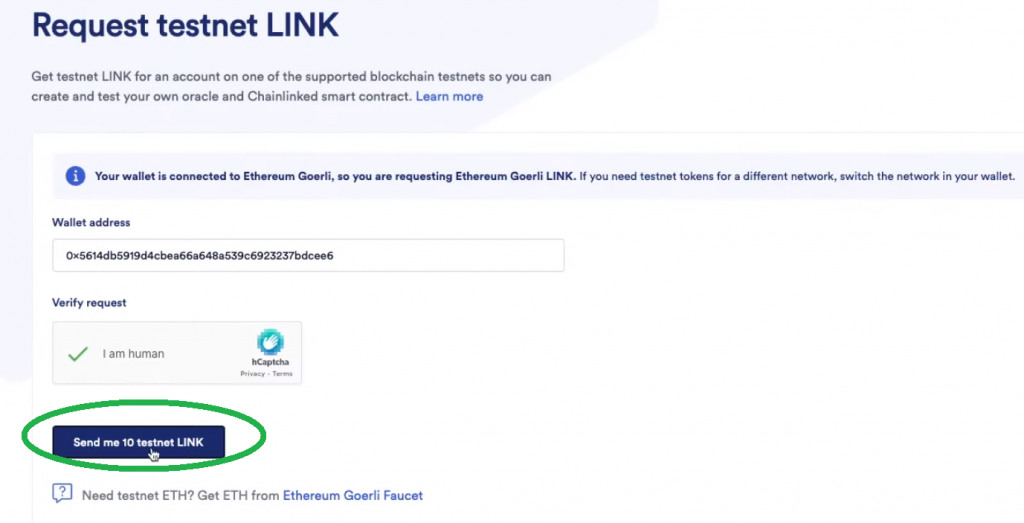
Subsequent, return to “vrf.chain.hyperlink“ and choose your subscription:
On the following web page, use the “Add Funds” button:
Then, add ten testnet LINK to your subscription:
Word: After clicking on the “Verify” button, you will need to verify the switch of tokens together with your MetaMask.
By finishing the above steps, it is best to have an energetic subscription with a steadiness of ten LINK tokens prepared:
You’ll use your subscription ID and the funds to get a random quantity through the use of the Chainlink VRF good contract. You may entry that good contract template through the “Get random quantity documentation web page”:
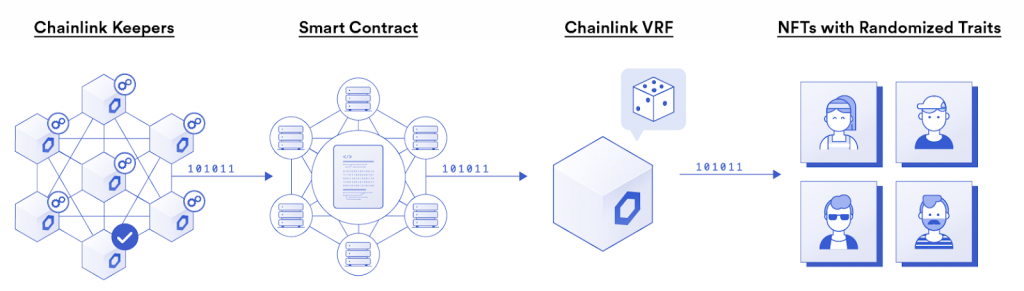
Use the video above (6:56) for a fast code walkthrough of that VRF contract template. All in all, “requestRandomWords” is the operate that generates the randomness and the “fulfillRandomWords” operate executes the motion primarily based on the obtained random quantity. Then, use Remix to deploy that good contract (7:50):
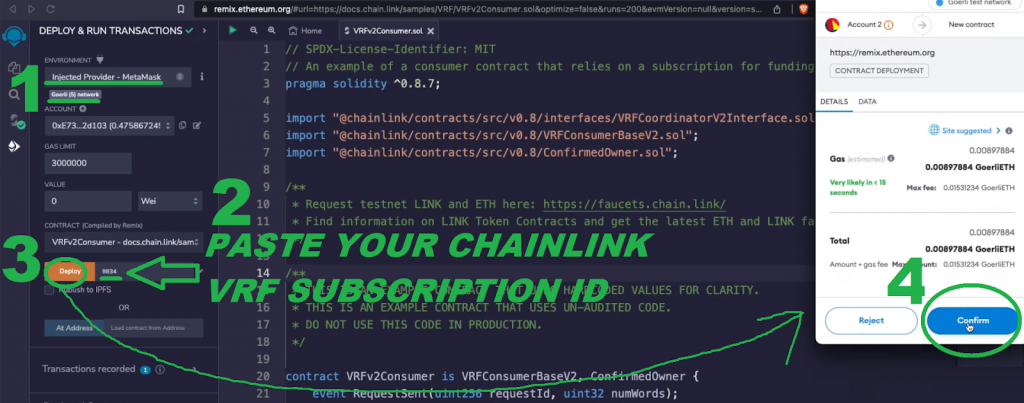
After you’ve deployed your occasion of the above good contract, you’ll have the ability to copy its deal with:
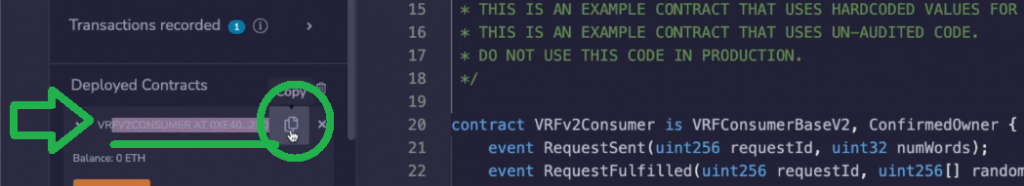
With the deployed contract deal with copied, return to your Chainlink VRF subscription web page and add a brand new shopper:
Construct a Chainlink NFT Sensible Contract
Now that you know the way to arrange your Chainlink VRF subscription and use it for the template contract, it’s time you do that for our instance NFT good contract: “RandomNFT.sol“. Use the video above (9:32) to comply with together with our in-house professional as he writes this contract, or copy the entire code from GitHub through the “RandomNFT.sol” hyperlink.
This contract incorporates Chainlink VRF’s randomness for minting our three instance NFTs and is designed to construct a Chainlink NFT. So, its objective is to create an ERC721 token primarily based on deciding on one in all our NFT metadata recordsdata. These recordsdata additionally embrace URLs pointing to our three instance photos. Each the NFT-representing recordsdata and metadata recordsdata are saved in IPFS. For the sake of this tutorial, you should use our recordsdata; nevertheless, you may additionally use your personal recordsdata.
Word: In fact, you can too go together with a larger variety of NFTs than simply three, however in that case, you must tweak the code accordingly.
Storing Pictures and Metadata to IPFS
Whether or not you resolve to make use of Brownie or Remix, you must have your NFT-representing recordsdata and corresponding metadata in IPFS. For the aim of importing photos, producing metadata recordsdata utilizing photos’ URLs, and importing metadata to IPFS, we created two Python scripts: “ipf_img.py” and “ipfs-upload.py“. The primary one uploads the pictures to IPFS, whereas the second assemble the metadata recordsdata and uploads them to IPFS. Right here’s one in all our three instance metadata recordsdata already uploaded to IPFS:
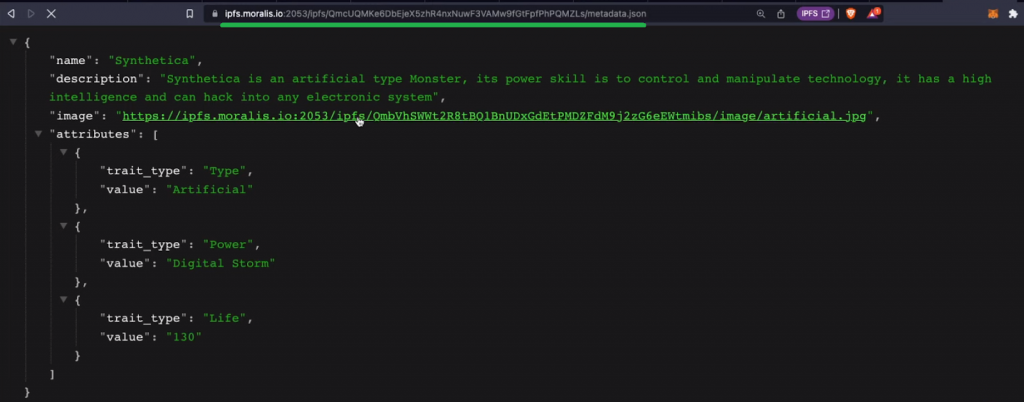
So, if you wish to create your distinctive NFTs, you must have your photos contained in the “img” folder and tweak the descriptions within the “ipfs-upload.py” script accordingly. Moreover, each of those scripts use Moralis’ “evm_api.ipfs.upload_folder” technique. As such, ensure that to get your Web3 API key and retailer it inside a “.env” file below “MORALIS_API_KEY“. You may get your API key from the Moralis admin space in these two steps:
Word: Should you want extra steering with importing your recordsdata to IPFS, use our video information on learn how to add NFT collections to IPFS.
Deploy Your Solidity Sensible Contract with Brownie or Remix
Our “RandomNFT.sol” contract is constructed to be deployed with Brownie. For the deployment objective through this technique, we’ve a number of scripts: “helpful_script.py“, “deploy_random_nft.py“, and “brownie-confi.yaml” (30:08). Contained in the latter, you must add your Chainlink VRF subscription ID:
To make use of these deployment scripts, you additionally want a personal pockets key, Infura mission ID, and Etherscan API key. Be certain that to retailer these variables inside one other “.env” file:
Word: Should you want steering with acquiring these variables, use the video on the prime of the article, beginning at 34:00.
With all the above in place, you’re able to deploy your good contract utilizing the next command line:
brownie run scripts/deploy_random_nft.py --network goerli
In case you’re not conversant in Brownie, you may as a substitute use Remix to deploy your good contract. In that case, the code requires some minor tweaks, so ensure that to make use of the “RandomNFTForRemix.sol” script as a substitute.
Whichever deployment technique you utilize, ensure that to repeat your deployed contract’s deal with and use it so as to add a brand new shopper to your Chanlink VRF subscription, identical to we did for the “VRF” contract template above.
Construct Frontend and Backend Parts of an NFT Minting Dapp
To wrap up our Chainlink NFT tutorial, you will need to additionally construct a easy frontend JavaScript dapp and a easy backend Python dapp. In fact, you don’t have to code the required scripts from scratch. As an alternative, you should use our full code that awaits you on GitHub. To finish the method, you want the above-deployed good contract’s deal with and ABI. You may comply with our in-house professional’s lead to do that with the assistance of the “update_frontend.py” script (38:57).
So far as the frontend goes, “App.js” does the trick (40:16). That is the place we import the ethers.js Web3 library and use its modules to cowl the Web3 performance behind the “Join Pockets” and “Mint!” buttons of our frontend.
Relating to the “Get My NFTs” button, you get to make use of the facility of Moralis’ API and implement the ultimate of the three code snippets showcased within the intro of at present’s article. For this objective, we use the “companies.py” script:
from moralis import evm_api
import os
from dotenv import load_dotenv
load_dotenv()
api_key = os.getenv("MORALIS_API_KEY")
def get_nft_owners(deal with: str):
params = {
"deal with": deal with,
"chain": "goerli",
"format": "decimal",
"restrict": 100,
"cursor": "",
"normalizeMetadata": True,
}
end result = evm_api.nft.get_nft_owners(
api_key=api_key,
params=params,
)
return end result
To make the above script work, you will need to get the linked pockets deal with from the frontend. That is the place the “view.py” script enters the scene. Don’t overlook so as to add the “get_owners/” endpoint to your mission settings (contained in the “urls.py” script). Lastly, to see how the “App.js” script makes use of the on-chain knowledge fetched with the “evm_api.nft.get_nft_owners” technique, use the video on the prime (44:23).
Construct a Chainlink NFT
By following the steps outlined within the earlier part together with the above video, it is best to have the ability to construct a neat random NFT minter. On the frontend, our instance dapp is fairly easy; it solely has three buttons:

As soon as we click on on the “Join Pockets” button, the MetaMask extension pops up, asking us to pick our account:

With the account chosen, we have to click on on the “Subsequent” button. Within the second step, we lastly join our pockets through the “Join” button:

After efficiently connecting our pockets, the “Join Pockets” button modifications to “Linked”. Then, we are able to use the “Mint!” and “Get My NFTs” buttons. The primary one will set off our good contract and mint one of many three random NFTs we used as examples. It is going to additionally assign possession to the linked Web3 pockets. Since minting an NFT requires an on-chain transaction, the “Mint!” button triggers MetaMask, the place we have to verify the minting transaction and canopy the fuel charges:

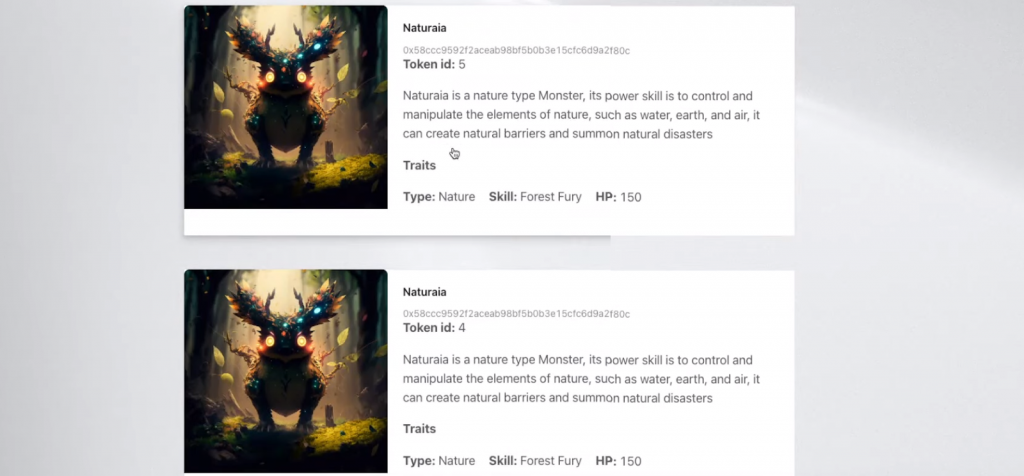
If we hit the “Get My NFTs” button, our dapp shows all of the NFTs owned by the linked wallets that have been minted utilizing this mission’s good contract on the backside of the web page. For instance, this linked pockets owns two NFTs:
Exploring Chainlink and NFTs
If you wish to be taught the ins and outs of NFTs, we advocate you dive into the “NFT” content material that awaits you on the Moralis weblog. There, you’ll have the ability to discover the fundamentals in addition to extra detailed facets, akin to studying concerning the distinction between the ERC721 and ERC1155 token requirements. In terms of exploring Chainlink and its merchandise, the official Chainlink web site and the Chainlink documentation are the assets to make use of. Nevertheless, you should use the next sections to cowl the important fundamentals to take advantage of out of at present’s Chainlink NFT tutorial.
What’s Chainlink?
Chainlink is a decentralized community of oracles constructed on the Ethereum blockchain. The core objective of Chainlink is to facilitate the switch of tamper-proof knowledge from off-chain sources (real-world knowledge) to on-chain good contracts. Tamper-proof inputs, outputs, and computations that Chainlink offers assist superior good contracts. Because of Chainlink, conventional programs can hook up with the rising blockchain business. This could generate extra safety, effectivity, and transparency in social and enterprise processes. Chainlink oracles collectively retrieve knowledge from a number of sources, mixture it, and ship a validated, single knowledge level to the good contract to set off its execution. Because of this, it removes any centralized level of failure.
Present Chainlink merchandise embrace market and knowledge feeds, VRF, automation, proof of reserve, and cross-chain bridging (CCIP). They provide numerous use instances, together with randomizing NFTs, as utilized in our instance mission above.
What’s a Chainlink NFT?
A Chainlink NFT is a non-fungible token whose creation in some way includes Chainlink. On the one hand, which means that a Chainlink NFT makes use of one in all Chainlink’s merchandise, akin to VRF, in its creation course of. That is the kind of NFT we created in at present’s tutorial. Listed below are two examples of NFTs using Chainlink:
- Using Chainlink’s market and knowledge feed:
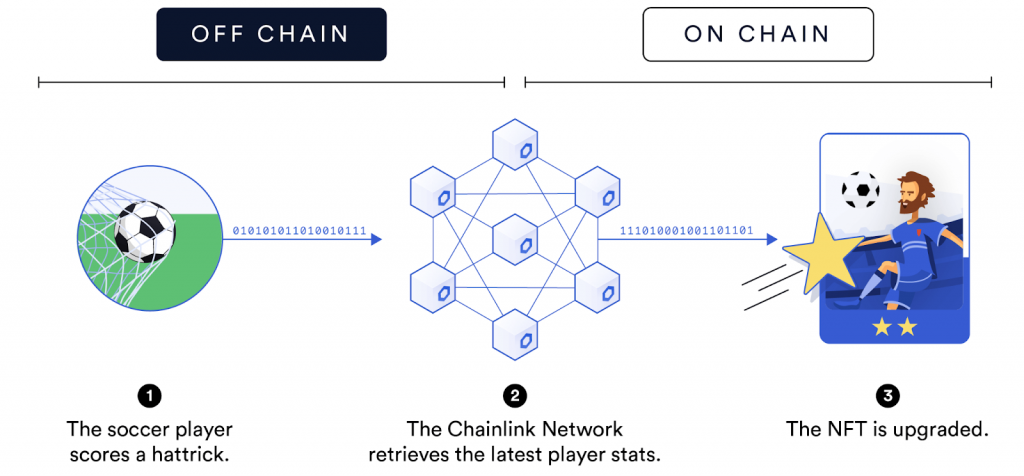
- Using Chainlink’s VRF:
Alternatively, a Chainlink NFT can be a non-fungible token that was created by the Chainlink core group or one other Chainlink-associated celebration. These sorts of Chainlink NFTs usually embrace Chainlink emblems, akin to the brand. Right here’s an instance:

Exploring “Chainlink Construct Deploy NFT” Instruments
Should you adopted alongside within the above tutorial, you used a number of highly effective Web3 growth instruments that every one play an important function within the “Chainlink construct deploy NFT” feat. So, let’s rapidly cowl every of these instruments:
- Chainlink VRF – That is one in all Chainlink’s merchandise that gives cryptographically safe randomness. It’s the device to make use of everytime you need to introduce true randomness into blockchain-based initiatives.
- MetaMask – MetaMask is the main Web3 pockets that comes within the type of a cellular software and browser extension. The latter can be a must have device for Web3 devs. It allows you to connect with dapps, verify on-chain transactions when deploying or interacting with good contracts, ship and obtain crypto belongings, and extra. As such, MetaMask is a vital “Chainlink construct deploy NFT” device.
- Visible Studio Code (VSC) – VSC is arguably the most well-liked IDE and code editor.
- Brownie – Brownie is a Python-based growth and testing framework. It lets you create, deploy, confirm, and take a look at good contracts that focus on Ethereum Digital Machine (EVM).
- Remix – Remix is a web based IDE that lets you write, deploy, confirm, and work together with good contracts utilizing your favourite browser.
- Ethereum Faucet – An Ethereum faucet is a crypto faucet offering “take a look at” crypto belongings for Ethereum testnets. For instance, in at present’s tutorial, we targeted on the Goerli testnet. Should you’d like extra data on Goerli, test our information exploring learn how to get Goerli ETH.
- Moralis – Moralis is the final word Web3 API supplier that empowers you to create all types of dapps the straightforward approach. That stated, Moralis makes a speciality of instruments wanted by crypto wallets and portfolio trackers. Moralis provides the Web3 Auth API, Web3 Streams API (for good contract and crypto pockets monitoring), and the final word Web3 Knowledge API. What’s extra, they’re all accessible with a free Moralis account.
Chainlink NFT Tutorial – Construct a Chainlink NFT – Abstract
In at present’s article, you had a chance to construct a Chainlink NFT minting dapp that makes use of an array of NFT-representing recordsdata and metadata recordsdata. You now know that you may full this problem with the next 5 steps:
- Arrange your Chainlink VRF.
- Write your distinctive good contract script in Solidity or copy our template.
- Put together the NFT-representing and metadata recordsdata and add them to IPFS or use our instance recordsdata.
- Deploy your Solidity good contract that may construct a Chainlink NFT.
- Construct frontend and backend parts of an NFT minting dapp that ties all of it collectively.
Along with our Chainlink NFT tutorial, we additionally defined what Chainlink is and what a Chainlink NFT is. Additionally, we lined the gist of the instruments required to construct a Chainlink NFT. With the abilities and data obtained herein, try to be able to create your personal randomized non-fungible tokens.
If you wish to discover different blockchain growth subjects or deal with some beginner-friendly tutorials, ensure that to go to the Moralis documentation, the Moralis YouTube channel, and the Moralis weblog. A few of our newest subjects cowl an inventory of Web3 libraries, the wei to gwei conversion, and explores the “create ERC20 token” tutorial. Moreover, you may be taught extra concerning the Solana Python API, the Web3 get block operate, the perfect Polygon Mumbai faucet, and way more. Final however not least, if you wish to change into blockchain licensed, enroll in Moralis Academy. There, it is best to first be taught extra about blockchain and Bitcoin fundamentals.